GLOBAL BIOGEOCHEMICAL CYCLES of C,
N, P and S, MINERAL CYCLES (PATHWAYS,
PROCESSES BUDGETS) IN
TERRESTRIAL AND AQUATIC ECOSYSTEMS
The earth system involves interactions amongst the physical climate,
chemical cycles and living organisms. In
any ecosystem there is relationship between two major components. These are abiotic and biotic components. Biotic components represent all the living
organisms, which are plants, animals and microbes, while abiotic components
represent non-living and living components.
These components consist of lithosphere, hydrosphere and
atmosphere.
Hence recycling of matters
takes place in all these environments.
Actually living organisms require 40 necessary minerals, which get
deposited in the organic form in the body and later on, after death,
microorganisms decompose them. These
type of cycles, which depend on living organism and non living matter, are
called as "Biogeochemical cycle".
Actually this word consists of Bio + Geo, where Bio word is represent
living organisms, and Geo word is consist of geological forces, which may be
physical or chemical. Hence, the
movement of substances in between along the ecosystem is called as
biogeochemical cycle. Biogeochemical
cycle is of two types :
a. Those
cycles in which nutrient is found in gaseous form and atmosphere plays an
important role in
this cycle, then these are called as "atmospheric
cycle". Example - Carbon cycle.
Carbon Cycle
Carbon
is found in every living organism in the organic form, while in the environment
or atmosphere; it is present in the inorganic form. The main source of carbon is atmosphere,
where it is present in the form of CO2 in the concentration 0.345%
or 345 ppm. In the carbon cycle,
producers and decomposers are two major components, which regulate carbon
cycle.
In the carbon cycle, two processes
are very important :
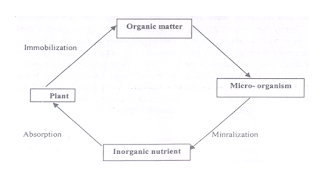
1. Immobilization: The process in which
inorganic carbon is converted into organic carbon; then it is called as
immobilization. Green plants regulate
this process only, because they convert CO2 into glucose in the
presence of sunlight and chlorophyll.
2. Minralization: The process in which organic carbon is
converted into inorganic carbon, is called as Minralization. This process is regulated by decomposers,
which are bacteria, fungi, nematodes etc.
In this process, inorganic carbon
gets converted into organic carbon i.e. glucose. This glucose gets transformed into various
forms as starch, cellulose, glycogen etc.
In plants it is stored in the form of starch. From plants these substances enter the food
chain and when herbivore eat plants, then organic contents gets into herbivores
and these enter from herbivores to carnivores.
Thus, these remain in organic form in the whole food chain. Although they get transferred from starch to
glucose and from glucose to glycogen, yet in each tropic level these organic
compounds gets oxidize during respiration due to which organic compounds
converts into CO2.
This CO2 enters into the
atmosphere, but a large part of organic compounds enters soil in the form of
excretory substances. Similarly after
death also, this compounds enter into the soil, where different types of
decomposers converts it in the form of complex organic compounds to simple
organic compound like starch and cellulose get converted into glucose. This gets decomposed in the presence of
cellulosic fungus, later on, during anaerobic decomposition, and then this gets
converted into alcohol and acids.
At last, these gets converted into CO2
by aerobic fungus and bacteria.
This CO2 reacts with
water and forms H2CO3, which forms carbonates from
rocks. Along with it, carbon deposits in
the form of coke, coal and petroleum, which later on are used in the form of
fuel and are released in the form of CO2 into the atmosphere which
is called as combustion.
Carbon cycle goes on in between
terrestrial zone, atmosphere and hydrosphere, in which global cycle shows 1015
gm carbon deposition.
Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen is an important nutrient
for plants and animals. 78% nitrogen is
found in atmosphere normally, but plants cannot absorb nitrogen directly from
atmosphere. They absorb it as ion from
the soil. Hence nitrogen can be divided
into two forms, available and unavailable from.
Gaseous form is unavailable form like N2, N2O, NO2,
NO etc., but ionic forms as NO2, NO3- and NH4+
of nitrogen are available form. Hence,
it is necessary for nitrogen to be converted from gaseous to ionic form. Then only, plants can absorb nitrogen. Nitrogen cycle is also a gaseous cycle. Following steps are important in nitrogen
cycle :
1. Nitrogen fixation: The process in which unavailable form of
nitrogen (gaseous) gets converted in to available form (ionic form), is called
as nitrogen fixation. This process takes
place by two ways. When nitrogen gets
fixed due to physical factors, then it is called as physical nitrogen
fixation. In this process nitrogen
converts into nitrate while if nitrogen gas is converted into fixed form
ammonium nitrogen with the help of living organisms, then it is called as biological
nitrogen fixation. This process is
regulated by microbes e.g.; Rhizobium, pseudomonas, cyanobacteria etc.
2. Minralization: The process in which
organic nitrogen is converted into inorganic nitrogen, is called as
Minralization. Since in this process,
the first product is ammonia, so it is called as ammonification. This process is anaerobic and is regulated by
ammonifying bacteria.
3. Nitrification: The process in which ammonia is converted in
to nitrate, it is called as nitrification.
This is an aerobic process, hence takes place in the presence of
oxygen. NH3, first of all,
converts into nitrite, Nitrosomonas.
Later on it regulates this process, and these nitrites get converted
into nitrates. Nitrobactor regulates
this process.
4. Denitrification: The process in which nitrate, nitrogen gets
converted into nitrogen gas, is called as denitrification. Denitrifying bacteria like pseudomonas
denitrificans controls this process. It
is an anaerobic process. The nitrogen
present in the atmosphere converts into ammonia or nitrate by physical or
biological nitrogen fixation and enters into the soil.
In
this form NH4+ or NO3--N is absorbed by plants and plants convert it
into organic nitrogen by Immobilization.
This organic nitrogen is in the form of amino acid and proteins in the
plants, which enter into animals through food chains. In the form of different animals and plants,
it enters into the soil, or after death, it enters into the soil. Here, Ammonifying bacteria degrade it and
change it into NH3. This NH3
gets oxidized and forms NO3--N.
This NO3--N
changes into N2 by denitrifying bacteria, which enters into the
atmosphere in the form of gas. Or NO3--N
enters into the underground water by the process of leaching.
Sulphur Cycle
Sulphur is an important compound
for plants and animals. It is found in
some amino acids like cytosine, methionine etc.
It is also an important constituent of proteins, hormones and
vitamins. Sulphur cycle is partially a
sedimentary cycle, whose most of the parts runs in the form of sediments, while
SO2 and SO3 are found in the atmosphere in the form of H2S
gas. Hence, in the soil and sediments,
its large reservoir pool is found and in small reservoir, it is in the form of
sediments. Following steps are involved
in this :
1. Immobilization: In this process, inorganic Sulphur gets
converted into organic Sulphur, which is called as immobilization. Green plants regulate this process.
2. Minralization: In this process organic Sulphur gets
converted into inorganic Sulphur. This
process takes place in the presence of microbes.
3. Reduction-Oxidation: In this process, SO2 or SO3
gets reduced in the form of H2S or H2S gets oxidized in
the form of SO2 or SO3.
In Sulphur cycle, sediments play
the major role. Due to microbial
activity, organic Sulphur gets converted into H2S and SO2
or SO3, which being water-soluble represents upward movement, which
can be absorbed by plants. This process
is called as microbial recovery. This
recovery is taking place mainly in the form of SO2 or SO3.
Similary, SO2 and SO3
are produced due to combustion of fossil fuels.
Volcano activation is the other source of SO2. This SO2 form SO3 in
the atmosphere by oxidation, which mixes with rainy water to form H2SO4.
This H2SO4
gives SO4-- ions, which later on enters the soil and form
the salts in the soil. Thus, Sulphur
again reaches back into the soil in the form of SO4--
from the atmosphere.
Organic S → H2S
2H2S + 3O2 → 2H2O +
2SO2
O2 + 2SO2 → 2SO3
H2O + SO3 → H2SO4
H2SO4 → 2H + SO4-
Ca++ + SO4- → CaSO4
Plants in the ionic form as S- or SO4-,
which is known as fixed Sulphur form, while SO2 and SO3
are gaseous form, which cannot be absorbed by plants, also absorb Sulphur. Mainly, Sulphur cycle depends on erosion,
sedimentation, leaching, rain adsorption like physical process and production
and decomposition like biological process.
Phosphorus Cycle
It is the simplest biogeochemical
cycle. Mainly, it is related with
lithosphere and hydrosphere, and atmosphere plays a negligible role in this cycle. Actually, phosphorous is present in the form
of PO4-3. It is
called inorganic form. A large amount of
phosphorous is found in the form of sedimentary deposit, which is 1000 times
more than the soil and ocean. Mainly,
the flow of phosphorous takes place in between the soil and ocean.
Mainly living organisms take the
inorganic form present inside the soil and after it is converted into organic
phosphorous by the process of biosynthesis.
But after the death of organism or after the excretion, dead organic
matter enters into the soil, where it is converted into inorganic phosphorous
by microbial activity. During rain, this
organic or inorganic phosphorous reaches in the water and it enters into the
ocean by the flow of river. In ocean,
dead organic phosphorous decomposes due to microbial activity, and when this
inorganic phosphorous is present in upper part of ocean, then it gets absorbed
by living organisms, but when it enters into the deep ocean, then its
sedimentation takes place, and then it forms the phosphate rocks.
Hence,
it is clear that very small amount of phosphorous takes part in this
cycle. Thus, its larger amount is
present in ocean or in soil. Its quality
is very less in fresh water. Similarly, amount of phosphorous in the different
biomass is very less. Although more
amount of phosphorous is present in aquatic biomass as compared to terrestrial
biomass.
It means that maximum part of
phosphorous is found in lithosphere and major part between or among the available
P is soluble in the ocean, which is absorbed by marine plants and animals,
excreted in the ocean itself. But this
phosphorous is taken out in the form of ocean plant and animal by the human
activity, which are used as weeds. These
are also used as fertilizers and on the land, if phosphorous enters into the
plants and animals or fertilizers are made from phosphate rocks and these
fertilizers enter from insects into the soil, among which is maximum part gets
deposited. Thus, phosphorous cycle is related only with lithosphere and
hydrosphere.











Comments
Post a Comment