PLASMA
MEMBRANE
Plasma membrane or biological membranes are composed
of lipids, proteins & small amounts of carbohydrates. The ratio of proteins
to lipid varies considerably among different membranes. Phospholipids are
present in almost all the membranes. Cholesterol is common in the membrane of
mamalian cells. Cardiolipin is found only in the inner mictochondrial membrane
.The plant plasma membrane has a high sterol to phospholipid molar ratio.
Carbohydrates are bound to the membrane in the form of glycoproteins when
attached to lipids. Carbohydrates are
not Langmuir present in the chloroplast lamellae, mictochondrial membrane s and
other membranes of cell organelles. The major component of the plant plasma
membrane is carbohydrates in the form of glycolipids, glycoproteins &
various cell wall polysaccharides. The plant cell membrane has to perform some
other functions than in animal cell, particularly in meditating the transport
of solutes into & out of the cell.
MODELS OF PLASMA MEMBRANE
Lipid Mono-layer Model Of Langmuir-
The first scientific attempt to know the membrane was
made by who suggested that membrane was composed of phospholipid of one
molecule thick. It was shown by an experiment in which the phospholipid was
spread on water. This form layer of one molecules thick on water surface.
Phospholipid are known as amphiphatic molecules which contain both hydrophilic
& hydrophobic regions .Langmuir interpreted his model that hydrophilic
or head groups of the lipid molecules
remain attach to the water surface and the hydrophobic tails remains free
towards the air.
Lipid Bilayer Model Of Gorter & Grendel-
Gorter & Grendel proposed a lipid bilayer model of
membranes structure from the experiments of RBC's. When lipid extracted from
RBC's where spread on the water surface, it was found that lipids were also
spread as one layer on water. But it covers twice the area on the water surface
than that the area of the cell from which lipid is extracted. The model of
Gorter & Grendel gives a new impetus to membrane research as they first
tried to describe the structure of membrane at the molecular level
The Danielli-Davson Model-They concluded that biological membrane could not be
of lipid alone. Danielli & Davson proposed a molecular model of the
membrane in which hydrophilic had groups of the lipid molecules is covered on
both of the side by a protein layer .The proteins are attached to the
hydrophilic head groups by lipid bilayer by ionic bonds . But in this model ,
the distance between ends of the fatty acid chains (hydrophobic tails)
is not specified
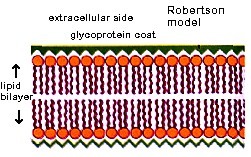
Robertson's Model Or Unit Membrane Hypothesis:-The presence of common structure in all biological
membrane led to postulate Unit membrane hypothesis .For detailed study of the
membrane structure & its molecular organisation , Robertson selected mylein
as its experimental sample .He selcted mylein rather than typical membrane
because in case of mylein , multiple layers of membrane are present which forms quasi-crystalline structure .He
carried out investigations on electron microscope using different stains for
lipid & proteins . He found that both
lipid & proteins are present in the membrane .Lipid are present in
two layers covered by proteins with lipid head groups projecting outward towards
both membrane surfaces .Robertson's observation corroborates the structure
proposed by Danielli & Davson .The
electron microscopic observations & X-rays diffraction data confirmed the
Danielli & Davson model of membrane structure
Fluid Mosaic Model-
In this model the main component is the lipid bilayer with hydrophilic groups
oriented towards outside & the hydrophilic groups towards inside of the
layer . The basic requirement for the basic requirements of the molecular
organisation of the membrane is free energy. The term fluid is given because
the lipid layer is present in the fluid state. The transition of fluid layer
from non fluid (gel) conditions to a liquid crystalline (fluid) state depends
on the temperature of the cell. According to this model, proposed by SJ Singer
& Jhon Nicholson, the principle of membrane organisation is as follows:
1. Lipids are present in
two layers.
2. Proteins are arranged
in two ways:
a)
Some are embedded in lipid layer, called
integral proteins &
b)
Some are present on surface of the lipid bilayer, called the peripheral
proteins.
3.
The lipid layer is usually in liquid crystal line, i.e., fluid state.
FUNCTION
- It forms protective covering over cytoplasmic
organelles.
- It is selective permeable in nature which allows
only selectable molecules to pass through it.
- Substance that pass through it by simple
diffusion,facilitated diffusion and by active transport method.
- Simple diffusion deives the net movement of
dissolved solutes as well as water molecules and the process is termed as
osmosis.
- Faciliated diffusion refers to the assisted
movement of a substance down its electrochemical gradient.
- Active transport is carried out by membrane
transport proteins.





Comments
Post a Comment